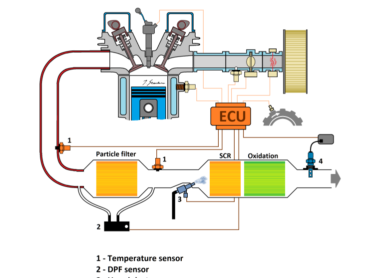
A NOx sensor, also known as a nitrogen oxide sensor, is an essential component in modern diesel engines. It is responsible for measuring the amount of nitrogen oxides (NOx) present in the exhaust gases, and communicating this information to the engine control unit (ECU) so that the engine can adjust its performance accordingly.
NOx is a group of highly reactive gases that are produced during the combustion process in diesel engines. These gases can have negative effects on both human health and the environment, as they contribute to the formation of smog and acid rain. In order to comply with emissions regulations, diesel engines must be designed to minimize the amount of NOx produced during operation.
The NOx sensor is typically located in the exhaust pipe, downstream of the catalytic converter. It works by measuring the amount of NOx present in the exhaust gases using a specialized ceramic material that reacts with the nitrogen oxides. This reaction generates an electrical current, which is then used to calculate the concentration of NOx in the exhaust.
The NOx sensor is an important part of the engine’s emissions control system. The sensor sends the information about the NOx level to the engine control unit (ECU), which then makes adjustments to the engine’s performance to reduce the NOx emissions. This can be achieved by adjusting the fuel injection timing, the air-to-fuel ratio, or by activating the catalytic converter.
Echo Feng
echo@best-growth.com